training - consulting - facilitating
get answers to some common questions


HACCP
The letters HACCP (pronounced ‘hassip’) are an acronym for the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point food safety risk assessment methodology. HACCP is used by the food industry worldwide to guide food safety program development and documentation.
The international ‘HACCP Standard’ is managed by the Codex Alimentarius Commission under the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) and is defined in the Annex of a document titled General Principles of Food Hygiene CAC/RCP 1-1969, Rev 4-2003.
HACCP is science-based and systematic in identifying specific hazards and their control measures, to ensure food safety. Although initially designed for application in food manufacturing, HACCP can be used throughout the supply chain from primary production to consumption.
HACCP requires a multidisciplinary approach to ensure all hazards are assessed and should include, where appropriate, expertise in agronomy, veterinary health, production, microbiology, medicine, public health, food technology, environmental health, chemistry and engineering according to the particular system under study.
The 7 principles of HACCP are:
-
1.Conduct a hazard analysis
-
2.Determine the Critical Control Points (CCPs)
-
3.Establish critical limit(s)
-
4.Establish a system to monitor control of the CCP(s)
-
5.Establish corrective action to be taken when monitoring indicates that a particular CCP is not under control
-
6.Establish procedures for verification to confirm that the HACCP system is working effectively
-
7.Establish documentation concerning all procedures and records appropriate to these principles and their application
A ‘HACCP Plan’ must conform to all 7 of these principles.
A ‘hazard’ is any biological, chemical or physical agent in, or condition of, food with the potential to cause an adverse health effect. Sometimes HACCP is also applied to identify and control hazards to product ‘quality’ aspects.
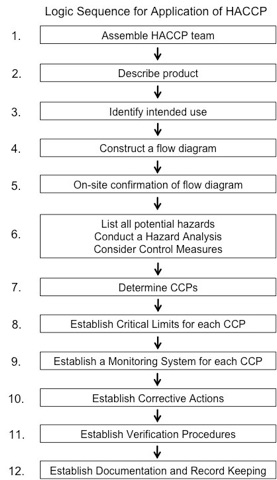
The Codex HACCP document also includes a Logic Sequence For Application of HACCP to guide the implementation of the system in a business. The following diagram shows the logic sequence which follows a 12 step process to ensure that the 7 HACCP principles are applied.
answers to some frequently asked questions about HACCP
to find out more - simply click on the icon links on these pages or click on the documents to download the files

click to download
Codex HACCP
care needs to be taken with using general decision trees such as this one - lest every step end up a CCP!
need signs?
get these free
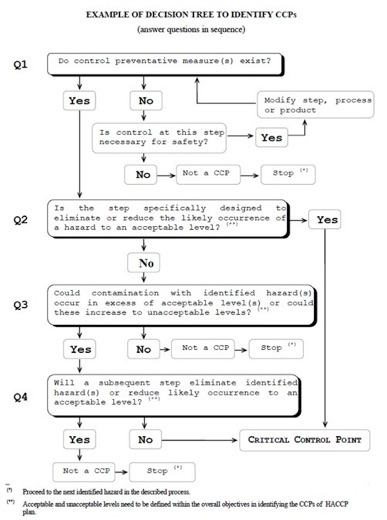
Decision trees can be useful tools for identifying whether a specific hazard that may occur at a step in the process flow diagram will determine that step to be a CCP. The following decision tree example is provided in the Codex HACCP guidance document.
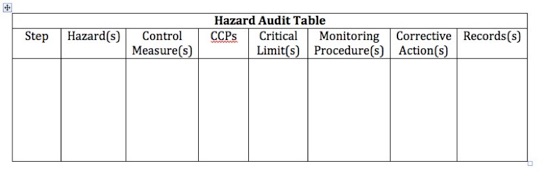
Information captured by the hazard analysis and determination of CCPs needs to be documented in the HACCP Plan, including product descriptions and specifications, process flowcharts, hazard audit tables (example shown below) and verification information.
The successful application of HACCP will always depend on the commitment of senior management to invest in employee training and support the implementation of HACCP Plan.
The successful application of HACCP will also depend upon the strength of the HACCP Pre-requisite Programs that underpin the HACCP Plan. HACCP Pre-requisite Programs include:
* Document Control * Standard Operating Procedures
* Training * Maintenance
* Cleaning & sanitation * Good Hygiene Practices
* Pest control * Calibration
* Approved Supplier Program
get the free
Adobe PDF Reader
computer can’t read PDF files?
© 2015 Frontline Services Australia Pty Ltd | ABN 41 136 738 997 ACN 136 738 997 | E: info@frontlineservices.com.au

